Increasing the thermomechanical stability of tangential fans for the use in thermoprocessing plants
Industrial Collective Research (IGF), 1 August 2019 to 30 April 2023
Project description
The production of modern materials requires precise temperature control during heat treatment. The processes for treating aluminium and copper materials as well as some types of steel with a treatment temperature of up to 800 °C are often carried out in high convection furnaces with forced circulation. This requires a high degree of temperature uniformity in the furnace. Since heat is transferred by convection, this results in the requirement for the largest possible and most uniform volume flow. Fans of various types are used in high convection systems, mainly axial and centrifugal fans; tangential fans have been the exception so far. The following table lists the most important properties (efficiency and maximum operating temperature) as well as advantages and disadvantages of the different fan types.
Comparison of fan designs
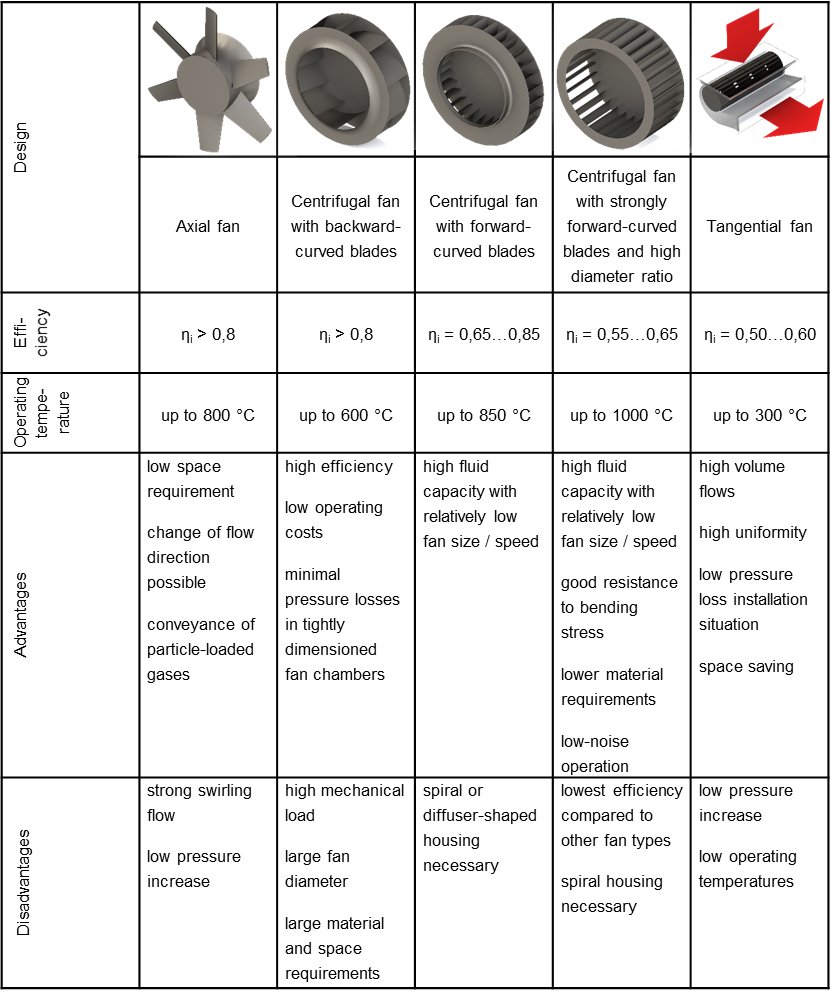
As an alternative to the fan types mainly used up to now, tangential fans are an option. Tangential fans are fans that suck in and blow out the process gas radially. For the same volume flow, tangential fans achieve a higher flow uniformity than a comparable centrifugal fan. The flow velocity is almost homogeneous across the width. This is a decisive advantage for use in thermoprocessing plants, since here a uniform volume flow is required over the entire furnace or zone width. In the previous IGF project 18418 N, it was shown that tangential fans fulfil the fluid dynamic requirements for use in typical industrial furnaces. The hot test rig set up in the previous IGF project 18418 N at the Department of Industrial Furnaces and Heat Engineering is suitable for investigating tangential fans at a process temperature of up to 500 °C. The tangential fan is flanged to a flow channel so that the fan module can be easily replaced. The air is conveyed in a closed circuit in the hot test stand. The system characteristic curve can be adjusted via a throttle device. Four co-rotating throttle valves are controlled by a linear actuator. The operating point can be set reproducibly by the position feedback of the electric cylinder. The test rig is heated via a 40 kW heating register with associated control. A thermocouple in the heating register is used as the controlled variable. There are two measuring points for flow measurement, one in the lower horizontal duct segment, at the outlet of the fan. Here, the outflow profile of the fan can be measured with local resolution. In case the volume flow cannot be determined precisely enough due to transient effects, another measuring point is provided in the upper horizontal section. Here the flow is rectified by two 90° baffles and the throttling.
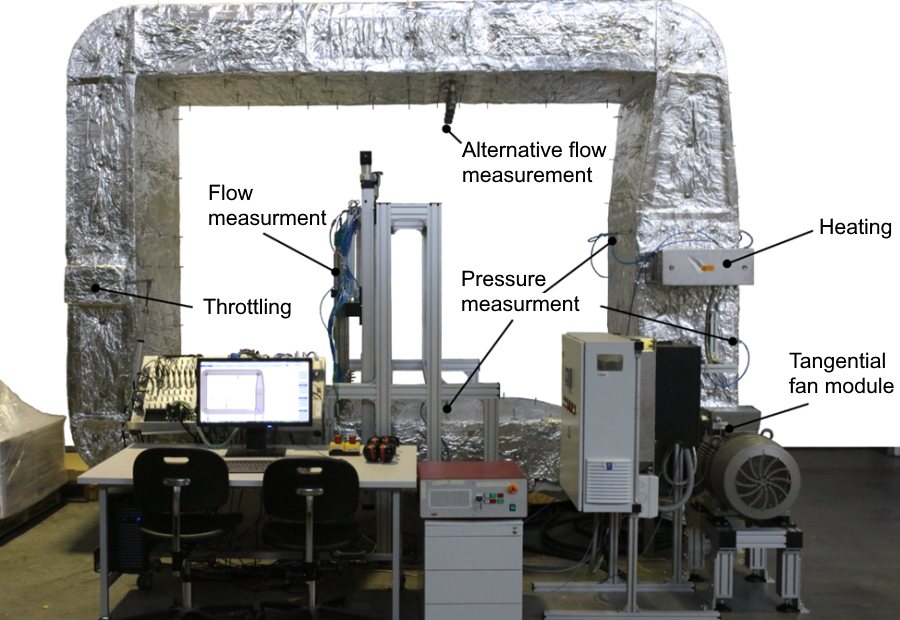
Tangential fan hot test rig at IOB
The aim of this project is to design a thermomechanically stable tangential fan for use in thermoprocessing plants. For this purpose, numerical investigations are carried out to increase the thermomechanical stability using the finite element method and the influence on the fluid mechanical properties using computational fluid dynamics. Based on the results of these investigations, a production sample is designed and manufactured. This functional sample will then be installed in the hot test stand, which has been supplemented with detailed sensor technology, and its flow and vibration behaviour will be investigated.
Based on the results of this project, plant manufacturers and suppliers should be able to adapt the design recommendations in order to build thermomechanically stable tangential fans. As a result, tangential fans should find wider application in convective heat treatment plants.
Project goals
- Numerical design of a cross-flow fan with focus on thermomechanical stability
- Numerical determination of the fluid mechanical properties of a cross-flow rotor with improved thermomechanical stability
- Design and manufacture of a functional sample
- Installation and commissioning of extended sensor technology for the investigation of the vibration behaviour of tangential fans on the existing hot test rig
- Experimental investigation of the vibration behaviour of the cross-flow fan functional sample
Contact

Funding

The project (project no. 20783 N) was submitted with the support of the Research Association of Industrial Furnace Manufacturers (FOGI) via the Forschungskuratorium Maschinenbau e.V. (FKM). It is funded via the German Federation of Industrial Research Associations „Otto von Guericke“ (AiF) in the program for Industrial Collective Research (IGF), initiated by the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action due to a resolution of the German Bundestag.
